Magnetic Force
Magnetic Force: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Magnetic Field, Magnetic Field Due to a Current, SI Unit of Magnetic Field, Non-SI Unit of Magnetic Field, Mass and Charge of Electron, Mass and Charge of Proton, Force on a Moving Charge in Magnetic Field, etc.
Important Questions on Magnetic Force
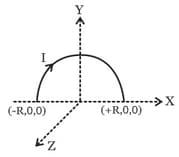
A semi circular current carrying wire having radius is placed in plane with its centre at origin . There is non-uniform magnetic field is existing in the region. The magnetic force acting on semi-circular wire will be along:
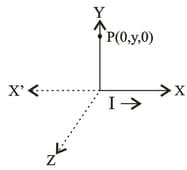
An electron moving with a velocity at a point in a magnetic field experiences a force . If the electron is moving with a velocity at the same point, it experiences a force . The force the electron would experience if it were moving with a velocity at the same point is
A charged particle is released from rest in a region of uniform electric and magnetic fields, which are parallel to each other. The locus of the particle will be
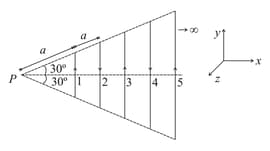
Infinite number of straight wires each carrying current I are equally placed as shown in the figure. Adjacent wires have current in opposite direction. Net magnetic field at point P is.
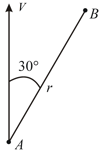
A charge particle of charge has velocity . When it passes through point and has velocity in the direction shown. The strength of magnetic field at point due to this moving charge is .
Two long parallel wires are at a distance 2d apart. They carry steady equal currents flowing out of the plane of the paper, as shown. The variation of the magnetic field B along the XX' is given by
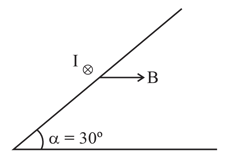
The figure shows a conductor of weight 1.0 N and length L = 0.5 m placed on a rough inclined plane making an angle with horizontal so that conductor is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of induction B = 0.1T. The coefficient of static friction between the conductor and the plane is 0.1, A current of I = 10A flows through the conductor inside the plane of this
paper as shown.
What is the force needed to be applied parallel to the inclined plane to sustain the conductor at rest.
The time period of ions in a cyclotron is independent of both the speed and radius of circular path.
A circular coil, of radius , carries a current . The expression for the magnetic field due to this coil at its centre is
A beam of particles projected along +x – axis, experiences a force due to a magnetic field along the +y – axis. What is the direction of the magnetic field?
An electron moves around the nucleus in a hydrogen atom of radius , with a velocity of . Calculate the following :
(i) The equivalent current due to orbital motion of electron.
(ii) The magnetic field produced at the centre of the nucleus.
(iii) The magnetic moment associated with the electron.
A circular coil of 200 turns and radius 10 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 05. T, normal to the plane of the coil. If the current in the coil is 3.0 A, calculate the
(a) Total torque on the coil.
(b) Total force on the coil.
(c) Average force on each electron in the coil, due to the magnetic field.
Assume the area of cross – section of the wire to be and the free electron density is .
An electron is moving along +ve x-axis in the presence of uniform magnetic field along +ve y-axis. What is the direction of the force acting on it?
What is the expression for the cyclotron frequency and does it depend on the speed of the charged particle?
In the SI system, B-field is measured in Tesla, denoted by T and H-field is measured in _____ per meter.
C.G.S. unit of magnetic field intensity is Gauss.
What are the non-SI unit of magnetic field?
What is the relation between Gauss and Tesla?
A small current element with and is centred at the origin. The direction of the magnetic field at position Westward from the origin will be
In the given figure at point . what is the direction of magnetic field.